The mechanism and evaluation method of fabric pilling
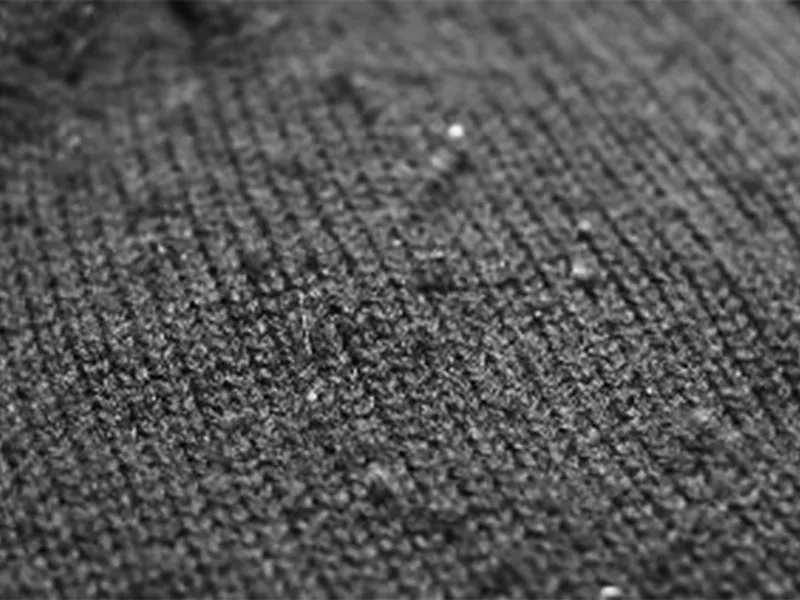
First, the mechanism of pilling The so-called fabric pilling refers to the formation of hair on the surface of the fabric by one or several fibers, and then entangled with each other in a spherical state. When the filament fabric is hooked on the surface, one or several hooked monofilaments are entangled with each other to form a ball. These hairballs not only affect the appearance, but also become the reason for the decline of styles such as feel. For the phenomenon of pilling, knitted fabrics with loose structure are most likely to occur.
According to research and observation, in the process of taking, the fibers of the fabric are first pulled out to form rings and hairs due to external friction. The condition for the hair to be pulled out must be that the external force is greater than the friction force of the fibers on the yarn. Therefore, strong twisted yarns or fibers with a larger friction coefficient for short fiber fabrics have greater resistance to fluffing, and are not easy to fluff. After the hairs reach a certain length, they can collide with each other to form a ball. Therefore, the length of the hairs pulled out has a great influence on the pilling of the fabric. In addition, the factors of pilling are the bending resistance, strength and wear resistance of the fiber. The fibers that are easy to bend are easily entangled into balls during the friction process, and the shedding of the hair balls depends to a large extent on the strength and wear resistance of the fibers. Some fibers have been worn or pulled off before forming longer fuzz, leaving only very short fuzz, which is not easy to form a ball. If the fiber's bending resistance and abrasion resistance are weak, the hairballs on the fabric surface will fall off quickly in the continuous friction.
As mentioned above, pilling can generally be divided into three stages; namely, the occurrence of hairs, the formation of hairballs, and the shedding of hairballs.
1. Since the premise of pilling is the generation of fluff, in addition to selecting suitable fiber raw materials and yarn processing conditions to make it difficult for fibers to be extracted from the fabric, the resin structure of the fabric can also improve the anti-pilling effect. However, this method can cause a stiff feel, so it is ideal to shed the hairs before they form a ball. If the fiber is modified to reduce the strength of the fiber, it will fall off after being rubbed, and it is not easy to form a ball.
2. Evaluation of fabric pilling For fabrics, it is most reasonable to evaluate the pilling resistance by the pilling density after friction, that is, the number of hair balls per unit area. However, since the size and shape of the hairballs are uncertain, if they are counted equally, the overall impression of the pilling fabric cannot be obtained. Therefore, the main method to measure the pilling degree of the fabric is to compare the pilled fabric with the standard sample to determine the pilling degree of the sample.
The domestic rating adopts a five-level system. The smaller the number, the more serious the fabric pilling is, and vice versa, the better the anti-pilling performance. When the sample is rated, there is a half-level first block between the levels as needed. As for the specific evaluation, there are two methods of eye rating and instrument rating. The rating method described in L only considers the form of pilling and does not consider the process after reaching the maximum degree of pilling, which is a defect.
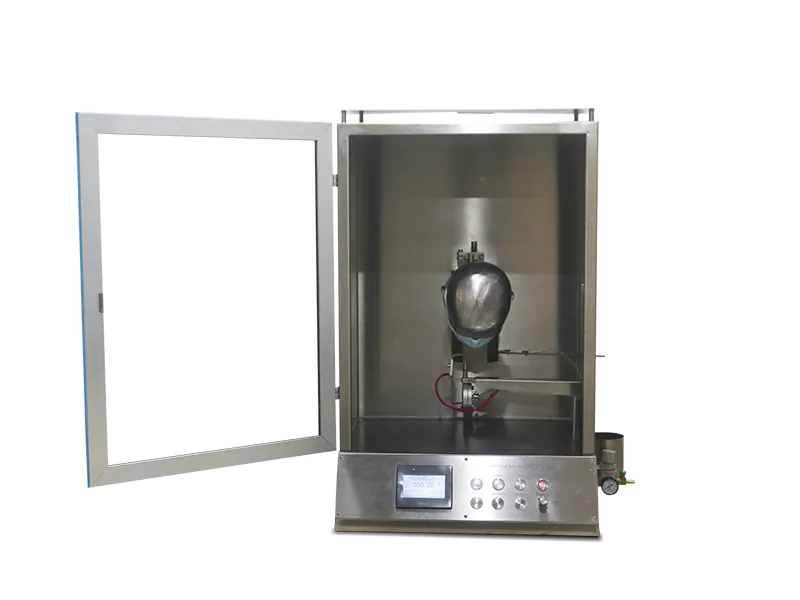
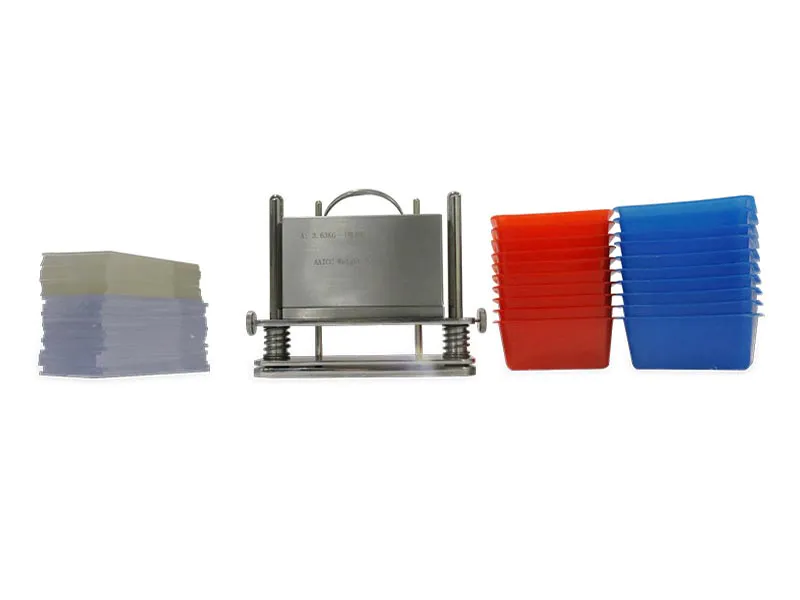
1. Pilling Box ICI Pilling and Snagging Tester GT-C18
ICI Pilling and Snagging Tester, to determine the surface pilling and snagging properties of both woven and knitted materials. ICI Pilling Box Tester complies in full with the requirements of EN ISO 12945-1 and BS 5811, etc.
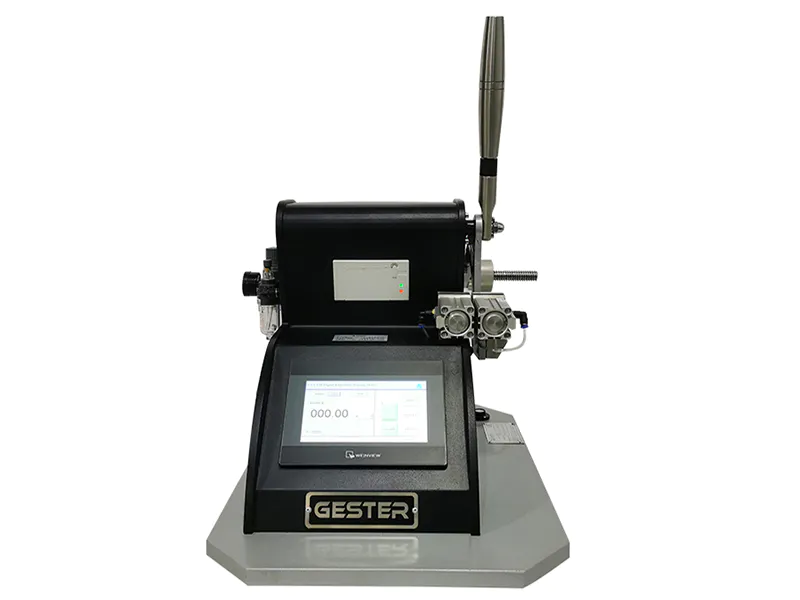
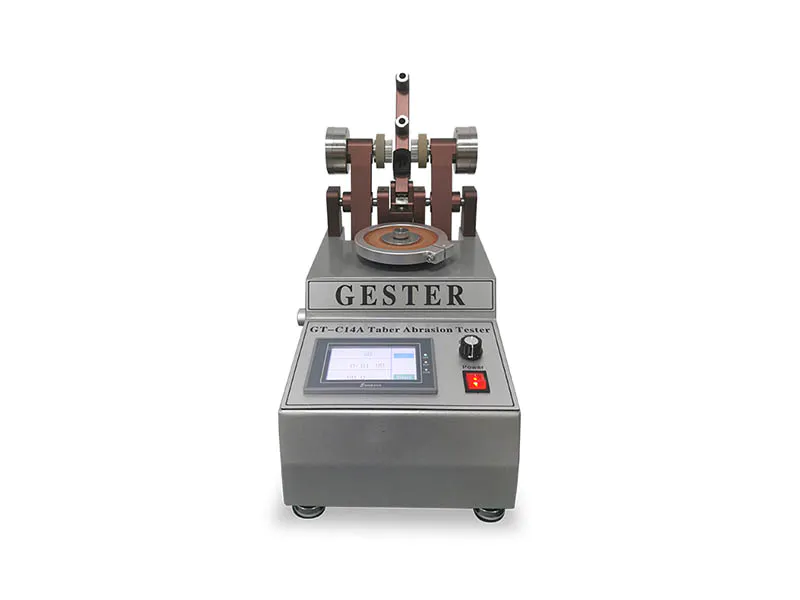
2. Martindale Abrasion and Pilling Tester GT-C13B
Martindale Tester to determine the abrasion and pilling resistance of all kinds of textile structures. Samples are rubbed against known abradents at low pressures and in continuously changing directions and the amount of abrasion or pilling is compared against standard parameters.
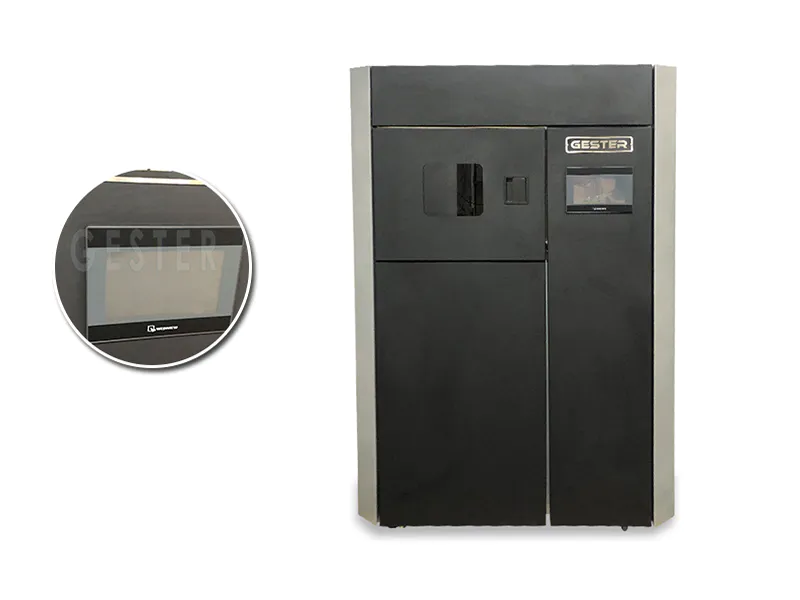
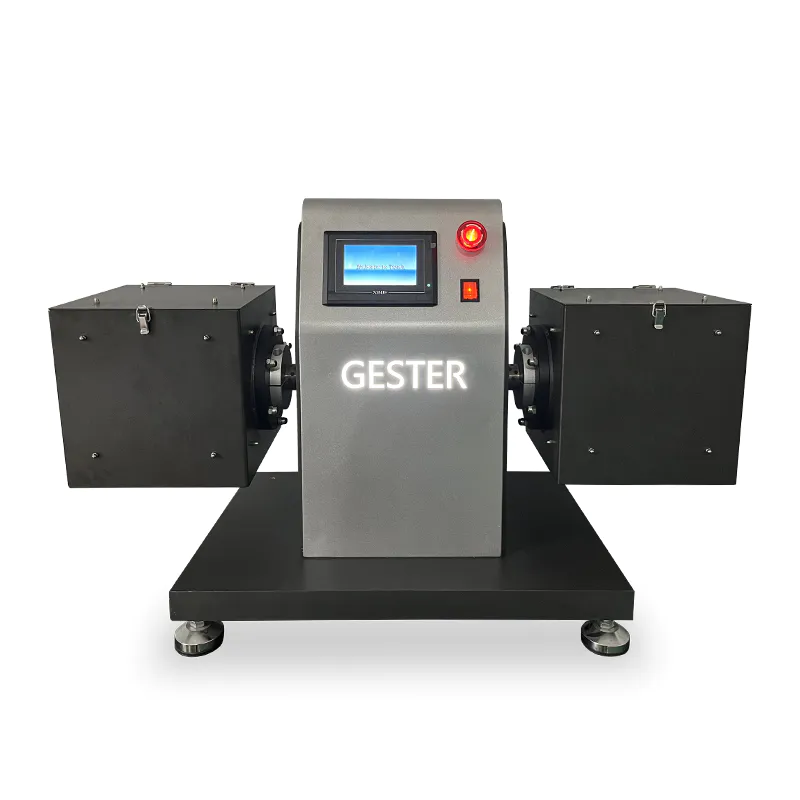
3. 4 Test chambers Random Tumble Pilling Tester GT-C19B
Random tumble pilling tester, to determine the pilling and fuzzing characteristics of textile fabrics. Precision high-speed impeller for agitating the test specimens against cork lining for a pre-determined time controlled by a timer and audible alarm. Compressed air is also injected into the chamber to assist in the tumbling action. Laboratory standard compressed air supply required.