textile testing
Test methods and procedures for rubbing fastness
by:GESTER Instruments
2021-06-11
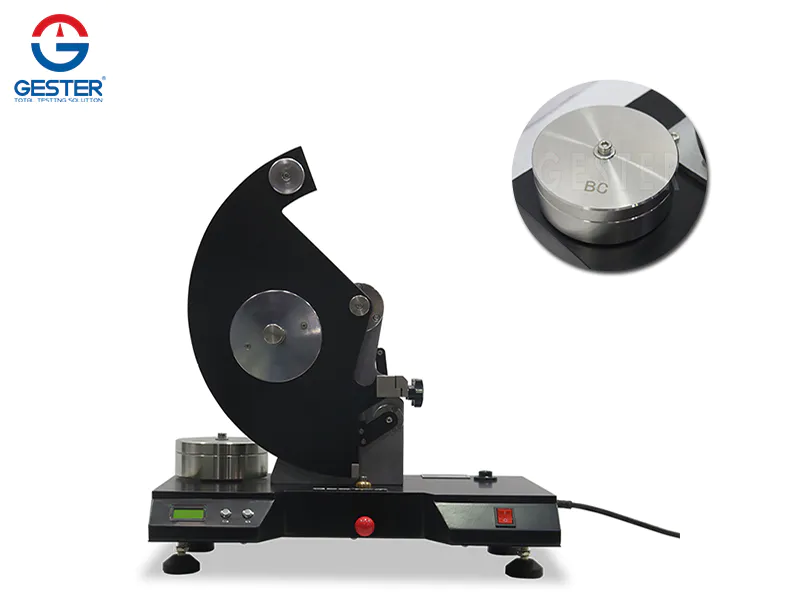
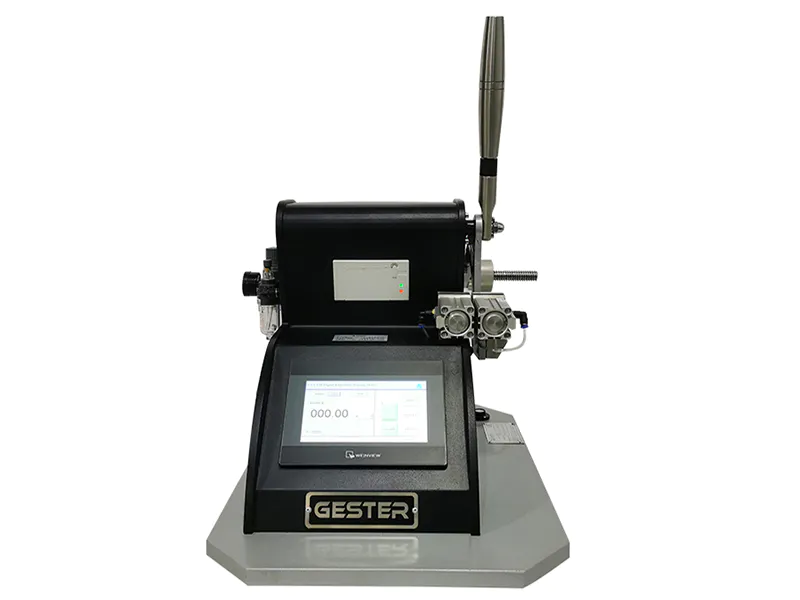
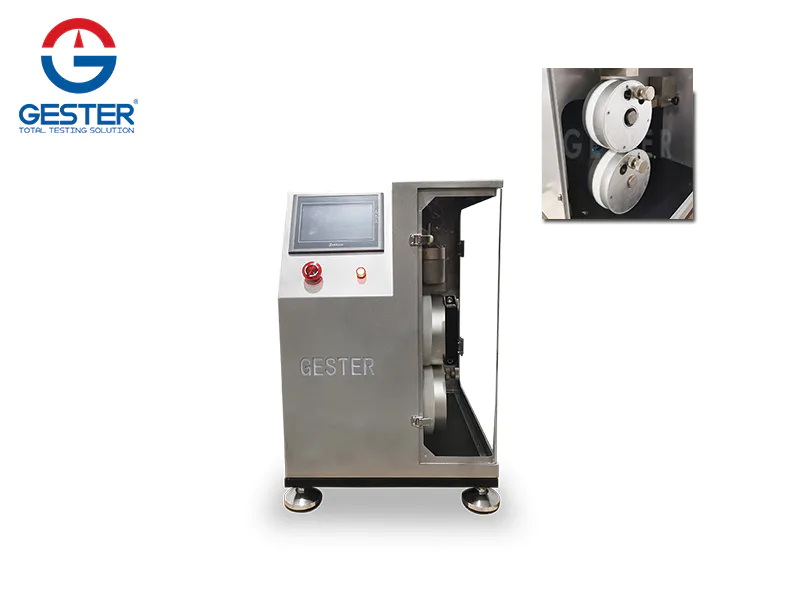
1. Purpose and scope A. This method is used to determine the degree of color transfer from the surface of the dyed textile to other surfaces by friction. Applicable to all textiles composed of various fibers; B. This test uses small square white friction cloth (dry and wet); C. Because soaping, dry cleaning, shrinking, ironing, finishing and other processes can affect The degree of color transfer of the material, so this method must be tested before or after treatment. 2. Principle a. The dyed sample is rubbed with the white rubbing cloth under fixed conditions; b. The degree of color transfer to the white cloth is evaluated by the AATCC staining gray ruler; 3. Definition: Slightly 4. Safety rules : Slightly five. Equipment and materials: A. AATCC friction device B. White friction cloth (5cm x 5cm) C. AATCC color transfer ruler D. Stained gray ruler E. White AATCC textile wet ink paper F. Sample holder 6. Calibration A. The accuracy of testing methods and equipment must be investigated regularly, and the results must be stored. In order to prevent incorrect results, the following observation and random inspection actions are important; B. Use a piece of cloth with poor rubbing fastness as a proofreader, and conduct three dry rub tests; (1) a very poor one The circular image has uneven dye adhesion, and rubbing your fingers at this time needs to be polished; (2) An overlapping elongated image indicates that the fastener has begun to loosen; (3) A reduced or striped friction image indicates that it is possible The rubbing cloth is placed on the rubbing finger when it is diagonally opposite; (4) If there is a rubbing mark on the sample, it means that the holder is placed too low; (5) If there is a straight line in the middle of the rubbing image and the direction of the rubbing is the same , Means that the friction bottom of the metal is not flat, and the friction bottom needs to be rearranged at this time; (6) If you use a cover plate, after covering the cover plate, move the front end of the rubbing finger to observe whether it touches the edge, and if there is any, move forward Cover plate; (7) Confirm whether the moisture absorption rate meets the standard; (8) If the rubbing sandpaper is too smooth or the sample slides on top, the sandpaper needs to be replaced; (9) Calibration work is very important; 7. Test sample: I. Two rubbing cloths (one dry and one wet). Note: If you want to take the average of multiple tests to improve accuracy, you need to use more friction cloth; II. Cut out at least 5cm x 13cm colored cloth and place it on the machine, with the long side perpendicular to the horizontal grain (knit cloth) 8. Conditioning Before the test, condition the colored cloth and rubbing cloth according to ASTM D1776 for at least 4 hours, condition 20±10C, 65±1%RH (relative humidity) 9. Steps: a. Dry friction: change the color The cloth is placed flat on the bottom of the friction device and covered with a cover to prevent sliding. Place the white rubbing cloth on the rubbing finger parallel to the rubbing direction, and put on the fastness fixture. Put down the rubbing finger at the front end, shake the handle for 10 revolutions (1 revolution/sec), and remove the rubbing cloth (note: if there are wool yarns or short fibers, they must be removed with transparent adhesive tape) b. Wet rubbing: rub the white first Wet it with steamed water, then take it out and put it into AATCC wet ink paper, reach the final moisture absorption rate of 65±5% by hand or a small pressing cylinder (note: prevent the moisture from evaporating and affect the moisture absorption rate), and then follow the dry Test by rubbing method, and finally dry at room temperature. c. Conditional according to ASTM D 1776 before rating. 10. Rating: Use AATCC stained gray ruler or color transfer ruler to evaluate the staining condition on the white friction cloth (note: if it is the average of multiple tests, take 1 decimal place to express) 11. Report a. Indicate whether it is dry friction test or wet friction test; b. Report the rating result; c. Indicate whether it is stained gray ruler or AATCC color transfer ruler for rating; d. Indicate what kind of treatment is before or after what kind of treatment; 2. Accuracy and deviation: slightly 13. Remarks: a. If it is a carpet, it must be tested by AATCC165; b. AATCC friction device is to imitate the movement of human fingers and forearms; c. AATCC friction device is designed to rub fingers (diameter 1.6cm) ) Back and forth movement, distance 10.4 ± 0.3cm each time, pressure 9N ± 10%d. Standard friction cloth specification fiber: 100% 10.3~16.8mm combed cotton; desizing, bleaching, no brightener or post-processing materials; yarn : 1.5 tex (tex) [40S/1 cotton] twist: 5.9 turns/cm [backhand twist (Z twist)] Fabric density: warp yarn 32 ±3 strands/cm, fiber yarn 33 ±3 strands/cm 1/1 plain weave ph value: 7±0.5 weight: 100±3g/m2 whiteness: Wu003d80 ±2 (measured by AATCC 110 method)
textile testing equipment has become a crucial product for marketers, especially when it comes to brand building and engaging potential customers.
Reach us at GESTER Instruments. We'll always try to give you the BEST deal on . If we can't, we'll at least give you some hel pful advice. Please use our experience!
To offer abundant options of product is an important factor to a company, such as textile testing equipmenttensile tester manufacturers to afford high-quality products for customers.
Many of the textile testing equipment listed here can be purchased for less money, but in general we recommend paying a slightly higher price for significantly improved performance. These are our top choices and their recommended configurations.
There have been conclusive evidence on 's role in tensile tester manufacturers and tensile tester manufacturers.
textile testing equipment has become a crucial product for marketers, especially when it comes to brand building and engaging potential customers.
Reach us at GESTER Instruments. We'll always try to give you the BEST deal on . If we can't, we'll at least give you some hel pful advice. Please use our experience!
To offer abundant options of product is an important factor to a company, such as textile testing equipmenttensile tester manufacturers to afford high-quality products for customers.
Many of the textile testing equipment listed here can be purchased for less money, but in general we recommend paying a slightly higher price for significantly improved performance. These are our top choices and their recommended configurations.
There have been conclusive evidence on 's role in tensile tester manufacturers and tensile tester manufacturers.
Custom message