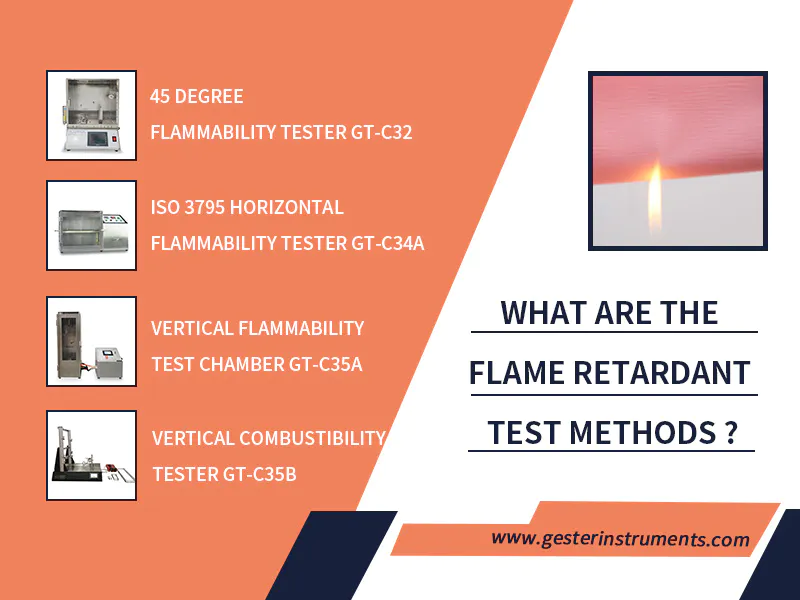
textile testing
Brief Analysis of the Test Experiment of Formaldehyde Content in Textiles
by:GESTER Instruments
2022-07-31
1. Experimental principle In the textile industry, formaldehyde is widely used in the dyeing and post-finishing processes of pure spinning or blended products (including some silk products) due to its use. The main function is to improve the durability of the auxiliaries on the fabric. However, because formaldehyde strongly stimulates the protoplasm of biological cells, it will cause respiratory inflammation and dermatitis. Therefore, it has been identified as a carcinogenic and teratogenic substance by the World Health Organization. The regulations or standards of various countries have made free formaldehyde content in textile products. Strict control [2]. This article uses GB/T2912.1—2009 'Determination of Formaldehyde in Textiles Part 1: Free and Hydrolyzed Formaldehyde (Water Extraction Method)' is based on the spectrophotometric method, and the experimental research and analysis are carried out from the details of the actual test process such as sampling, extraction, and placing time. . 2. Test procedure 1. Instruments and reagents Cary 50 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Varian, USA); ZHWY-110X50 water bath constant temperature shaker (Shanghai Zhicheng); electronic balance (0.001g); iodine volumetric flask (250 mL) ; Chromogenic test tube (10 mL); Graduated cylinder (100 mL). Formaldehyde standard solution: concentration of 11.0 mg/L (National Center for Standard Materials Research); tertiary water (or distilled water); color developer (Nessler's reagent): in a 1000 mL volumetric flask, add 150 g of ammonium acetate, and use 800 mL tertiary water was dissolved, then 3 mL of glacial acetic acid and 2 mL of acetylacetone were added, diluted to the mark with tertiary water, and stored in a brown bottle for more than 12 h. Ammonium acetate, glacial acetic acid, and acetylacetone were all of analytical grade. 2. Test principle The principle of water extraction method for the determination of formaldehyde content in textiles is to extract the textile fabrics in an aqueous solution at about 40 °C [3], the formaldehyde in the extract reacts with acetylacetone in Nessler's reagent, and the reaction equation is: CH2O+(CH3CO)2CH2→(CH3CO)2C=CH2+H2O The methylene group of acetylacetone is active because it has two carbonyl groups. It becomes a carbanion under the action of a base, attacks formaldehyde, and first becomes 3-hydroxymethyl-2,4- pentanedione ((CH3CO)2CH-CH2OH), followed by dehydration to give 3-methylene-2,4-pentanedione (yellow) product. Then use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance value at a specific wavelength (412 nm), and then obtain the formaldehyde content by referring to the standard working curve of formaldehyde. 3. Experimental method Take two samples from the sample and cut them into pieces, weigh 1 g respectively, accurate to 0.001 g, put them into a 250 mL iodine volumetric flask, add 100 mL of tertiary water, close the lid tightly, and put in (40 mL)±2) ℃ constant temperature shaking (60±5) min, filter the extract, pipette 5 mL of filtrate and 5 mL of chromogenic reagent into the chromogenic tube, and place it in (40°C).±2) Color development in a ℃ water bath (30±5) min, then take out and cool at room temperature (30±5) min, use a spectrophotometer to measure the absorbance at a wavelength of 412 nm [4]. 3. Results and Analysis 1. The influence of whether the sample is completely soaked during extraction on the test results of formaldehyde content Sample # and 2# float on the water surface without hand shaking after adding water, samples 3# and 4# are artificially hand shaking (about 30 s) after adding water to make the cloth sample completely immersed in water, and put 4 samples into the water at the same time. In the constant temperature water bath oscillator, under the same other test conditions, the test results of the formaldehyde content of the same fabric are shown in Table 1 due to the different infiltration degrees. Polyester cloth and nylon cloth (with coating) are mostly non-hydrophilic fabrics, so whether they are completely soaked in tertiary water during extraction has little effect on the test results of formaldehyde content; while the flocking that has been completely soaked by manual oscillation The results of cloth fabrics are nearly half higher than those without soaking; denim fabrics are usually immersed in the bottom of the water after adding water, and there is almost no possibility of floating on the water surface, so the effect of artificial hand shaking has no significant effect on the results. It is generally recommended that after adding 100 mL of tertiary water, the relevant testers should try to completely immerse the tested sample into the tertiary water (especially the fabrics such as flocking cloth or woolen wool), and then perform constant temperature oscillation extraction to ensure the test results. accuracy. 2. Influence of cooling time after oscillating extraction on the test results of formaldehyde content Under the same other test conditions, take 4 samples known to be different formaldehyde content grades (fabrics with the same composition analysis) respectively. After (40±2) ℃ constant temperature shaking (60±5) After min, the same sample was cooled at room temperature for 10 min, 25 min, 35 min, 45 min, and 60 min, and then the color development test was performed [5]. The results are shown in Table 2. Table 2 Test of formaldehyde content at different cooling times after extraction It can be seen from Table 2 that (1) Samples 1# to 4# have different results in formaldehyde content with different placement times. The formaldehyde content of 1# and 2# samples is low, and its influence with the change of storage time is also small, while the formaldehyde content of 3# and 4# samples is higher, and its influence with the change of storage time is more significant. (2) It is not that the longer the storage time, the higher the formaldehyde content. The formaldehyde content in a short period of time (within about 60 min) is an increasing trend. When the standing time continues to be prolonged (after 6 h), the formaldehyde content gradually decreases with the volatilization of moisture and formaldehyde itself.
In an age when textile testing equipment is increasingly important, the researchers believe manufacturers should pay close attention to their results.
GESTER International Co.,Limited is committed to attracting, developing, and keeping a diverse work force that reflects the nature of our global business.
It is never too late to have a new mindset and to get things moving in the right direction. Choose GESTER International Co.,Limited to be your quality provider.
There are ample scientific evidence of reducing the risk of tensile tester manufacturers.
The manufacturing industry is changing fast, so, for GESTER International Co.,Limited, being able to pivot and adapt as the marketplace shifts is imperative.
In an age when textile testing equipment is increasingly important, the researchers believe manufacturers should pay close attention to their results.
GESTER International Co.,Limited is committed to attracting, developing, and keeping a diverse work force that reflects the nature of our global business.
It is never too late to have a new mindset and to get things moving in the right direction. Choose GESTER International Co.,Limited to be your quality provider.
There are ample scientific evidence of reducing the risk of tensile tester manufacturers.
The manufacturing industry is changing fast, so, for GESTER International Co.,Limited, being able to pivot and adapt as the marketplace shifts is imperative.
Custom message