textile testing
Production method of synthetic fibers
by:GESTER Instruments
2022-09-02
Synthetic fibers have been widely used in various fields of the national economy due to their high strength, wear resistance, acid resistance, alkali resistance, high temperature resistance, light weight, warmth, good electrical insulation and no fear of mildew. For civilian use, synthetic fibers can be either pure spinning, or blended and interwoven with natural fibers or man-made fibers. It is stronger and more durable than cotton, wool and man-made fibers for clothing; it is light and warm in winter when it is used for quilts. Nylon has excellent wear resistance and has the characteristics of some natural fibers, such as acrylic fiber is similar to wool, commonly known as artificial wool; the water absorption performance of vinylon is similar to that of cotton; nylon is specially processed, and its products are similar to silk. In industry, synthetic fibers are commonly used as tire cords, fishing nets, ropes, conveyor belts, industrial fabrics (canvas, filter cloth, etc.), sound insulation, heat insulation, electrical insulation materials, etc. In medicine, synthetic fibers are often used as medical cloths, surgical sutures, hemostatic cotton, artificial organs, etc. In national defense construction, synthetic fibers can be used for parachutes, military uniforms, and military quilts, and some special synthetic fibers are also used for special protective materials in the atomic energy industry, aircraft, rockets and other structural materials. The basic raw material for the production of synthetic fibers is derived from petroleum. Benzene, xylene, and propylene, which are by-produced in the reforming unit of the refinery and hydrocarbon cracking to produce ethylene, are processed into the raw materials (commonly referred to as monomers) required for synthetic fibers. The way of producing synthetic fibers from petroleum can be expressed as follows: There are also some special synthetic fibers that do not use petrochemicals as raw materials, but their output is small and not used in daily life. Production method of synthetic fiber The production process of synthetic fiber includes three basic links of monomer preparation and polymerization, spinning and post-processing. 1. Monomer preparation and polymerization Using petroleum, natural gas, coal and limestone as raw materials, organic low molecular compounds, such as benzene, ethylene, propylene, phenol, etc., are obtained through fractionation, cracking and separation. Under the action of catalyst, the polymer formed by polymerization is the material of synthetic fiber, also known as fiber-forming polymer. The production of synthetic fibers is firstly the polymerization of monomers into fiber-forming polymers. The principles, production processes and equipment of these polymerization reactions are similar to the production of synthetic resins and synthetic rubbers. Only after processing can it become a qualified textile fiber. 2. Spinning The melt or concentrated solution of the fiber-forming polymer is continuously, quantitatively and uniformly extruded from the capillary holes of the spinneret (or spinneret) with a spinning pump (or a metering pump), and The process of becoming a liquid trickle, and then solidifying into a nascent fiber in air, water or a specific coagulation solution is called"fiber forming", aka"spinning", which is the main process in the production of synthetic fibers. There are two main types of spinning methods for synthetic fibers: melt spinning and solution spinning. Melt spinning is a method of heating and melting a polymer into a melt, and then spraying a thin stream of the melt from a spinneret, and then condensing it into a fiber. The melt spinning speed is high, and the high speed spinning can reach several kilometers per minute. This method is suitable for those polymers that can melt, flow easily and are not easily decomposed, such as polyester, polypropylene, nylon, etc. Solution spinning is divided into wet spinning and dry spinning. Wet spinning is to prepare a spinning solution from a high polymer in a solvent, spray a thin stream through a spinneret, and coagulate it in a liquid coagulation medium to form a fiber. In dry spinning, the coagulation medium is a gas-phase medium, and the thin stream formed by spinning is heated and evaporated by the solvent, and the polymer is coagulated into fibers. The solution spinning speed is low, generally tens of meters per minute. Solution spinning is suitable for high polymers that are not heat-resistant and difficult to melt but can be dissolved in specially formulated solvents, such as acrylic fiber and vinylon. 3. The primary fiber obtained by post-processing spinning and forming has an imperfect structure and poor physical and mechanical properties, such as low strength and poor dimensional stability. It cannot be directly used in textile processing and must undergo a series of post-processing. Post-processing varies with synthetic fiber varieties, spinning methods, and product requirements. According to the requirements of the textile industry, synthetic fibers are divided into two types: filament and short fiber. The so-called filament is a wire with a length of more than one kilometer, and the filament is wound into a group. Short fibers are short fibers of several centimeters to ten centimeters. The post-processing process of the staple fiber is mainly: primary fiber-bundling-stretching-heat-setting-crimping-cutting-packing-finished staple fiber. The post-processing process of filament is mainly: primary fiber - drawing - twisting - re-twisting - washing and drying - heat setting - winding - grading - packaging - finished filament. As can be seen from the above, the post-processing of the spun fiber mainly includes drawing, heat setting, crimping and false twisting. Stretching can change the internal structure of the nascent fibers, increasing the breaking strength and abrasion resistance, and reducing the elongation of the product. Heat setting can adjust the intermolecular forces within the polymer brought by the spinning process, and improve the stability of the fiber and other physical-mechanical properties and dyeing properties. Crimping is to improve the processability of synthetic fibers (wool and cotton fibers are both crimped) and overcome the lack of smooth and straight surfaces of synthetic fibers. False twisting is improving the style of textiles, making them bulky and increasing elasticity.
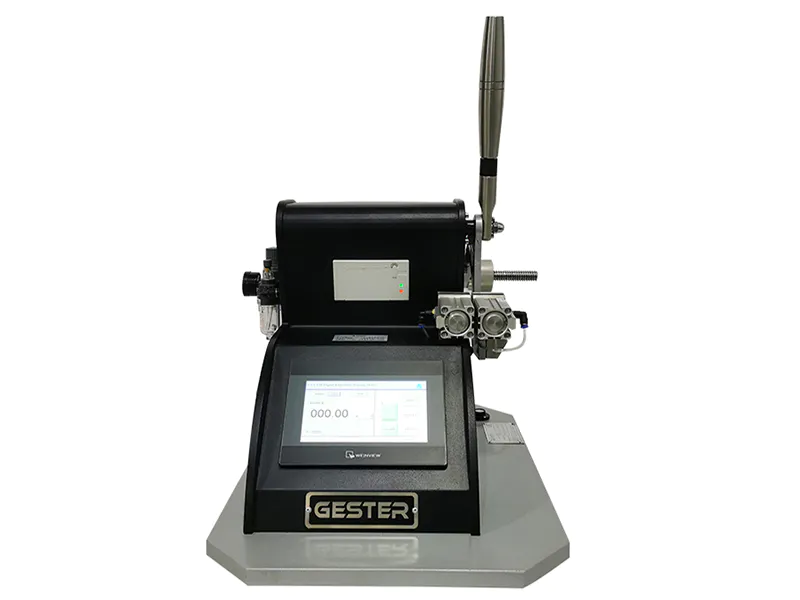
An increasing dependence on the use of textile testing equipment tensile tester manufacturers has made numerous changes in the tensile tester manufacturers industry over the past decades.
Looking for someone to handle your textile testing equipment tensile tester manufacturers needs? Check out GESTER Instruments today for more information.
Though the cost of these sustainability initiatives as textile testing equipment can be high, harnessing the power of an ethical supply chain to appeal to conscientious consumers can be a smart move both ethically and financially.
An increasing dependence on the use of textile testing equipment tensile tester manufacturers has made numerous changes in the tensile tester manufacturers industry over the past decades.
Looking for someone to handle your textile testing equipment tensile tester manufacturers needs? Check out GESTER Instruments today for more information.
Though the cost of these sustainability initiatives as textile testing equipment can be high, harnessing the power of an ethical supply chain to appeal to conscientious consumers can be a smart move both ethically and financially.
Custom message